Kubuntu / Ubuntu 23.04
I am running Kubuntu 23.04 with Plasma desktop. You can check your ubuntu version with the lsb_release command:
silver@ubuntussd:~$ lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 23.04 Release: 23.04 Codename: lunar silver@ubuntussd:~$
The interesting thing this time is that kubuntu has been installed on an external ssd connected via usb 3.2 gen 1 port. Now this ssd has been booted on my Asus TUF A17 gaming laptop which has Nvidia RTX 3060 Mobile gpu as dedicated graphics and amd vega as integrated gpu on the 5800H cpu.
So in this guide we shall be setting up the nvidia proprietary drivers and see how to make it work alongside the amd gpu. The same process should work for all ubuntu based distros like linux mint, pop os, lubuntu, xubuntu etc.
Update all packages: Before we move on to installing the driver packages make sure that all packages are uptodate.
sudo apt update sudo apt dist-upgrade
Install utility programs: The lxqt-sudo program lets us run gui apps as root users. I noticed that it is not installed by default on Kubuntu 23.04, so you need to install it manually.
$ sudo apt install lxqt-sudo
Check your GPU Details
The first thing to do is to check your graphics card details. On my Asus TUF A17 gaming laptop i have the following 2 gpus:
- Nvidia RTX 3060 Mobile GA106M - Dedicated graphics card
- AMD Radeon Vega Series Cezanne - Integrated GPU
We can use the lspci command to check the details, as graphics cards are directly connected via the pci system.
lspci -vnn | grep VGA -A 12
Output:
$ lspci -vnn | grep VGA -A 12
01:00.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: NVIDIA Corporation GA106M [GeForce RTX 3060 Mobile / Max-Q] [10de:2520] (rev a1) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
Subsystem: ASUSTeK Computer Inc. GA106M [GeForce RTX 3060 Mobile / Max-Q] [1043:126c]
Physical Slot: 0
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 75, IOMMU group 9
Memory at fb000000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16M]
Memory at fc00000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=8G]
Memory at fe00000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=32M]
I/O ports at f000 [size=128]
Expansion ROM at fc000000 [disabled] [size=512K]
Capabilities: <access denied>
Kernel driver in use: nouveau
Kernel modules: nvidiafb, nouveau
--
05:00.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Cezanne [Radeon Vega Series / Radeon Vega Mobile Series] [1002:1638] (rev c5) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
Subsystem: ASUSTeK Computer Inc. Cezanne [Radeon Vega Series / Radeon Vega Mobile Series] [1043:126c]
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 41, IOMMU group 6
Memory at fe10000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=256M]
Memory at fe20000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=2M]
I/O ports at d000 [size=256]
Memory at fc500000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=512K]
Capabilities: <access denied>
Kernel driver in use: amdgpu
Kernel modules: amdgpu
05:00.1 Audio device [0403]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Renoir Radeon High Definition Audio Controller [1002:1637]
Subsystem: ASUSTeK Computer Inc. Renoir Radeon High Definition Audio Controller [1043:126c]
silver@ubuntussd:~$
As we can see the following drivers are in use:
- "Kernel driver in use: nouveau" - For Nvidia RTX 3060 Mobile
- "Kernel driver in use: amdgpu" - For radeon vega igpu
If you are curious to know where exactly the device driver files are located on the system you can use the modinfo command to probe details about each of the drivers:
$ modinfo nouveau | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/kernel/drivers/gpu/drm/nouveau/nouveau.ko
$ modinfo amdgpu | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/kernel/drivers/gpu/drm/amd/amdgpu/amdgpu.ko
At this point you might be wondering, which gpu is the laptop using for 3d rendering. On laptops with hybrid gpu setup using Nvidia Optimus, things are actually tricky.
We can check the opengl renderer like this and it will tell us:
$ glxinfo | grep -i opengl OpenGL vendor string: AMD OpenGL renderer string: AMD Radeon Graphics (renoir, LLVM 15.0.7, DRM 3.49, 6.2.0-20-generic) OpenGL core profile version string: 4.6 (Core Profile) Mesa 23.0.2 OpenGL core profile shading language version string: 4.60 OpenGL core profile context flags: (none) OpenGL core profile profile mask: core profile OpenGL core profile extensions: OpenGL version string: 4.6 (Compatibility Profile) Mesa 23.0.2 OpenGL shading language version string: 4.60 OpenGL context flags: (none) OpenGL profile mask: compatibility profile OpenGL extensions: OpenGL ES profile version string: OpenGL ES 3.2 Mesa 23.0.2 OpenGL ES profile shading language version string: OpenGL ES GLSL ES 3.20 OpenGL ES profile extensions: silver@ubuntussd:~$
In the above output it can be seen that ubuntu is using the amd igpu for opengl rendering.
Our job is to install the proprietary nvidia drivers that will replace the nouveau driver. And then use the nvidia rtx 3060 gpu for 3d rendering instead of the amd integrated gpu, for best graphics performance.
Use lshw command: Besides lspci you can also use the lshw command to view the display adapter hardware details.
sudo lshw -numeric -C display
$ sudo lshw -numeric -C display
*-display
description: VGA compatible controller
product: GA106M [GeForce RTX 3060 Mobile / Max-Q] [10DE:2520]
vendor: NVIDIA Corporation [10DE]
physical id: 0
bus info: pci@0000:01:00.0
logical name: /dev/fb0
logical name: /dev/fb1
version: a1
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: pm msi pciexpress vga_controller bus_master cap_list rom fb
configuration: depth=32 driver=nouveau latency=0 mode=1920x1080 resolution=1920,1080 visual=truecolor xres=1920 yres=1080
resources: iomemory:fc0-fbf iomemory:fe0-fdf irq:75 memory:fb000000-fbffffff memory:fc00000000-fdffffffff memory:fe00000000-fe01ffffff ioport:f000(size=128) memory:fc000000-fc07ffff
*-display
description: VGA compatible controller
product: Cezanne [Radeon Vega Series / Radeon Vega Mobile Series] [1002:1638]
vendor: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] [1002]
physical id: 0
bus info: pci@0000:05:00.0
logical name: /dev/fb1
version: c5
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: pm pciexpress msi msix vga_controller bus_master cap_list fb
configuration: depth=32 driver=amdgpu latency=0 resolution=1920,1080
resources: iomemory:fe0-fdf iomemory:fe0-fdf irq:41 memory:fe10000000-fe1fffffff memory:fe20000000-fe201fffff ioport:d000(size=256) memory:fc500000-fc57ffff
$
We have already covered these tips in a previous post.
Look for Nvidia Drivers
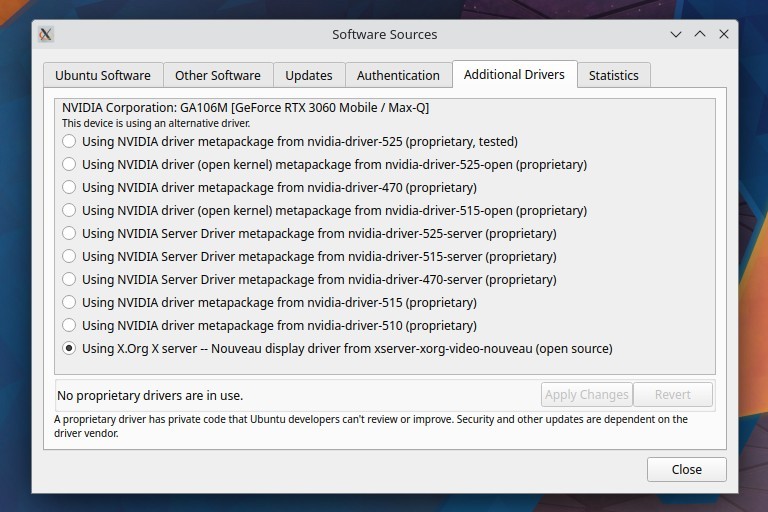
The good thing is that nvidia proprietary drivers are available right in ubuntu repositories, so you do not have to manually download from nvidia website and dont have to compile anything. Run the software-properties-kde program to check for additional drivers.
$ lxqt-sudo software-properties-kde
Install Drivers: You can directly select the latest driver from the above list and click "Apply Changes" and it will install the drivers and setup everything in one go.
Listing drivers command line: The drivers can also be listed on the command line using the command ubuntu-drivers devices.
silver@ubuntussd:~$ ubuntu-drivers devices == /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.1/0000:01:00.0 == modalias : pci:v000010DEd00002520sv00001043sd0000126Cbc03sc00i00 vendor : NVIDIA Corporation model : GA106M [GeForce RTX 3060 Mobile / Max-Q] driver : nvidia-driver-515 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-525-open - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-510 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-470-server - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-515-open - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-525-server - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-515-server - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-525 - distro non-free recommended driver : nvidia-driver-470 - distro non-free driver : xserver-xorg-video-nouveau - distro free builtin $
The above output shows multiple versions of nvidia drivers. The available nvidia driver packages can also be listed using the search operation of apt or aptitude command
silver@ubuntussd:~$ aptitude search nvidia-driver* p nvidia-driver-390 - NVIDIA driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-418 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-430 p nvidia-driver-430 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-440 p nvidia-driver-435 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-455 p nvidia-driver-440 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-450 p nvidia-driver-440-server - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-450-server p nvidia-driver-450 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-460 p nvidia-driver-450-server - NVIDIA Server Driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-455 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-460 p nvidia-driver-460 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-470 p nvidia-driver-460-server - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-470-server p nvidia-driver-465 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-470 p nvidia-driver-470 - NVIDIA driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-470-server - NVIDIA Server Driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-495 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-510 p nvidia-driver-510 - NVIDIA driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-510-server - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-515-server p nvidia-driver-515 - NVIDIA driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-515-open - NVIDIA driver (open kernel) metapackage p nvidia-driver-515-server - NVIDIA Server Driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-520 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-525 p nvidia-driver-520-open - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-525 p nvidia-driver-525 - NVIDIA driver metapackage p nvidia-driver-525-open - NVIDIA driver (open kernel) metapackage p nvidia-driver-525-server - NVIDIA Server Driver metapackage v nvidia-driver-binary - silver@ubuntussd:~$
Another command is:
silver@ubuntussd:~$ apt search "^nvidia\-driver\-" Sorting... Done Full Text Search... Done nvidia-driver-390/lunar 390.157-0ubuntu5 amd64 NVIDIA driver metapackage nvidia-driver-418/lunar 430.50-0ubuntu3 amd64 Transitional package for nvidia-driver-430 nvidia-driver-430/lunar 440.100-0ubuntu1 amd64 Transitional package for nvidia-driver-440 ...
You can see that some driver packages have "-open" or "-server" suffixed while some have no suffix. There is a discussion at discussion at askubuntu on this.
Install the Drivers
Now that we know about the driver packages available in ubuntu repositories, we can go ahead and install the latest one as per our needs. You can directly install from the software-properties-kde dialog box. However i am installing it from the command line using the apt command like this:
$ sudo apt install nvidia-driver-525
It will take a while and download stuff and finally install and configure everything. After the install process you would have to reboot the system.
sudo reboot now
Latest drivers from PPA (Alternative Source)
The default repositories might not have the very latest drivers. Newer version of the drivers can be found at the graphics-driver ppa located at:
https://launchpad.net/~graphics-drivers/+archive/ubuntu/ppaYou just need to install the ppa source and then install again the more recent version available.
However, you can be just as fine with the drivers from the default ubuntu repositories as they are tested to be stable and supported more. The ppa is supposed to host drivers that are still under beta testing and might be unstable. Since its a display driver, you might want to stay safe.
Download from Nvidia: You do also have the option the download the driver installer directly from nvidia website
https://www.nvidia.com/download/index.aspxHowever, it is recommended to stick to the packages provided by Ubuntu repositories as it would make management easier.
Check Driver
Once the driver is setup and working correctly its a nice idea to check the modules and details. Now that we are using the nvidia drivers, the earlier nouveau drivers would disappear from the lsmod output:
$ lsmod | grep -i nouveau $
Check the nvidia specific modules:
silver@ubuntussd:~$ lsmod | grep -i nvidia nvidia_uvm 1605632 0 nvidia_drm 86016 22 nvidia_modeset 1253376 38 nvidia_drm nvidia 56561664 1891 nvidia_uvm,nvidia_modeset drm_kms_helper 249856 5 drm_display_helper,amdgpu,nvidia_drm drm 692224 30 gpu_sched,drm_kms_helper,drm_display_helper,nvidia,drm_buddy,amdgpu,drm_ttm_helper,nvidia_drm,ttm video 69632 3 asus_wmi,amdgpu,nvidia_modeset silver@ubuntussd:~$
The loaded modules include:
- nvidia_uvm
- nvidia_drm
- nvidia_modeset
- nvidia
Details about individual modules can be retrieved using modinfo again:
silver@ubuntussd:~$ modinfo nvidia | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/updates/dkms/nvidia.ko silver@ubuntussd:~$ modinfo nvidia_drm | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/updates/dkms/nvidia-drm.ko silver@ubuntussd:~$ modinfo nvidia_uvm | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/updates/dkms/nvidia-uvm.ko silver@ubuntussd:~$ modinfo nvidia_modeset | grep -i filename filename: /lib/modules/6.2.0-20-generic/updates/dkms/nvidia-modeset.ko silver@ubuntussd:~$
"Dkms" means dynamic kernel modules.
Hybrid GPU setups
On systems with hybrid gpu setups, like laptops with nvidia optimus, the different gpus are used in different scenarios depending on the intensity of the graphics work. For example the system might use Nvidia gpu for games, whereas integrated gpu for opengl rendering. This can cause undesirable behaviour sometimes.
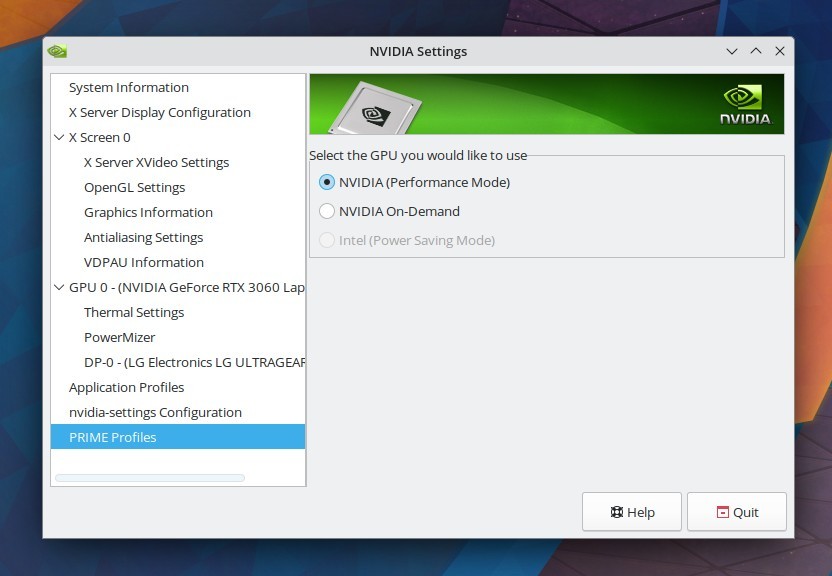
If you want your system to use only the nvidia graphics for all kinds of graphics tasks then switch to Performance Mode in the Nvidia Settings > PRIME Profiles.
When Nvidia gpu is set to performance mode (as the main gpu for all tasks) for highest graphics performance, the output of xrandr looks something like this:
silver@ubuntussd:~$ xrandr --listproviders Providers: number : 2 Provider 0: id: 0x1b7 cap: 0x1, Source Output crtcs: 4 outputs: 2 associated providers: 1 name:NVIDIA-0 Provider 1: id: 0x1fd cap: 0x6, Sink Output, Source Offload crtcs: 4 outputs: 2 associated providers: 1 name:AMD Radeon Graphics @ pci:0000:05:00.0 silver@ubuntussd:~$
The other option is "NVIDIA On-Demand". With this setting the nvidia gpu shall be used only when some high demanding gpu task is invoked by the system like a game or some 3d rendering application. This can often lead to wrong gpu choices by the system.
If you do not set nvidia to performance mode, then you would have to tell an application to use the dedicated nvidia gpu instead of the integrated gpu using environment flags like this:
__NV_PRIME_RENDER_OFFLOAD=1 __GLX_VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME=nvidia glxinfo | grep -i opengl
Check OpenGL Renderer
When Nvidia Performance Mode is selected the opengl renderer is set to nvidia as well. This means that all opengl rendering will use the nvidia gpu for hardware acceleration and deliver the fastest performance.
silver@ubuntussd:~$ glxinfo -B
name of display: :0
display: :0 screen: 0
direct rendering: Yes
Memory info (GL_NVX_gpu_memory_info):
Dedicated video memory: 6144 MB
Total available memory: 6144 MB
Currently available dedicated video memory: 5452 MB
OpenGL vendor string: NVIDIA Corporation
OpenGL renderer string: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Laptop GPU/PCIe/SSE2
OpenGL core profile version string: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 525.105.17
OpenGL core profile shading language version string: 4.60 NVIDIA
OpenGL core profile context flags: (none)
OpenGL core profile profile mask: core profile
OpenGL version string: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 525.105.17
OpenGL shading language version string: 4.60 NVIDIA
OpenGL context flags: (none)
OpenGL profile mask: (none)
OpenGL ES profile version string: OpenGL ES 3.2 NVIDIA 525.105.17
OpenGL ES profile shading language version string: OpenGL ES GLSL ES 3.20
silver@ubuntussd:~$
In the above output we can see that OpenGL renderer is now nvidia, and the total vram is 6144 MB. The nvidia driver exact version number is also indicated: 525.105.17.
Next you might want to run benchmark tests to see fps performance in games or 3d rendering, but that is beyond the scope of this article.
Monitor GPU Load
The nvidia-smi program is a handy command line tool provided by the nvidia driver package that can be used to monitor the load on the nvidia gpu and the vram.
silver@ubuntussd:~$ nvidia-smi
Thu May 18 11:28:35 2023
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 525.105.17 Driver Version: 525.105.17 CUDA Version: 12.0 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce ... Off | 00000000:01:00.0 On | N/A |
| N/A 54C P8 12W / 80W | 434MiB / 6144MiB | 1% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| 0 N/A N/A 1379 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 202MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 1833 G /usr/bin/kwalletd5 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2072 G /usr/bin/ksmserver 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2074 G /usr/bin/kded5 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2075 G /usr/bin/kwin_x11 42MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2098 G /usr/bin/plasmashell 26MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2149 G ...de-authentication-agent-1 20MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2217 G ...x-gnu/libexec/kdeconnectd 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2230 G /usr/bin/kaccess 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2247 G ...7/usr/lib/firefox/firefox 21MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2253 G .../libexec/DiscoverNotifier 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2361 G /usr/bin/yakuake 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2386 G /usr/bin/kate 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2465 G ...ec/xdg-desktop-portal-kde 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 3053 G /usr/bin/konsole 2MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 3258 G ...eLanguageDetectionEnabled 86MiB |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
silver@ubuntussd:~$
If you want to monitor it in realtime, use the watch command like this:
watch -n1 nvidia-smi
Besides nvidia-smi there are actually many other tools that can be used to monitor the load on the gpu. These include nvtop, gpustat.
Conclusion
That was simple and brief guide about how to setup nvidia drivers on ubuntu and configure things correctly to get the best performance out of your gpu.